INTRODUCTION
University of Somalia (UNISO), which was established in 2005 by independent scholars, is a private higher education institution which is categorically non-political, non-partisan, and non-sectarian. The establishment of the UNISO came at a time when the chances of post-secondary education available for Somali children who had completed their secondary education were very limited due to the protracted unrest and statelessness that have prevailed in Somalia for over two decades.
The motives that impelled the founders of the UNISO were nothing more than establishing a credible, responsive, and sustainable higher education institution capable of contributing to the resilience and the societal development of Somali people through quality higher education in which career gaps among the young Somali generation are focused. UNISO aims at providing tertiary education study programs that are highly relevant to the market and social demands in its quest for better standards of living, justice, equity, and good governance in Somalia.
A great deal of time and effort has been devoted to the study of leaders and their leadership styles because leadership plays a critical role in a global environment. Ensuring the well-being of employees so that they can remain committed to their organizations is also another major challenge facing organizations today. There are very high costs associated with employee turnover, and to deal with these costs, organizations have to strive to create a bond between the employee and the organization (Johnson, 2008). Whichever way leadership and its pattern are defined, one thing that is certain and generally acknowledged among scholars is that, from time immemorial, the role of leaders in ensuring excellent organizational performance and workers commitment to work cannot be over emphasized. Those organizations that meet the needs of the employees and help them to become the best that they can be are more likely to have employees who are content and motivated and who in turn can be more committed to the organization.
In Canada, leadership has been always a crucial issue since organizations and companies are permanently in a constant struggle to be increasingly competitive. Leadership is an important function of management which helps to maximize efficiency and to achieve organizational goals. The word leadership has been described in terms of the position, personality, responsibility, influence process, instrument to achieve a goal, and behaviors.Most definitions have a common theme of directing a group toward a goal. Therefore, the leadership can be broadly defined as the relationship between an individual and a group built around some common interest wherein the group behaves in a manner directed or determined by the leader. Leaders can influence the behavior of their followers through the use of different styles, or approaches, to manage others. For the past three decades, a pair of predominant leadership styles (transactional and transformational leadership) has received a significant amount of attention.
On the other hand, employee commitment has long been a topic of interest to organizational researchers. One of the main reasons for its popularity is that organizations have continued to find and sustain competitive advantage through teams of committed employees. Many researchers found that an organization’s success is determined, in part, by having a high degree of organizational commitment. Organizational commitment has attracted considerable attention in theory and research because of its attempt to understand and clarify the intensity and stability of employee dedication to work organizations. Research literature states that organizational commitment is defined as a subordinate’s identification with the mission, goals, and vision of the organization. According to Eisenberg et al. (1983), organizational commitment has been defined in a variety of ways.
In Africa, the Kenyan government forms state corporations to meet both commercial and social goals. These corporations are very important to the Kenyan economy as they provide essential products and services to Kenyans and also offer employment to many people. State corporations in Kenya as is the case in most African countries have been faced with a myriad of challenges. There are a number of problem indicators which include absenteeism from work, lateness, corruption, theft, a high rate of complaints, low quality work output, and high turn-over of professional staff. Some public servants do not attend to customers efficiently as it is still possible to find long queues of people waiting to be served while there is no one in the office. Miring’u (2011) also notes that state corporations face challenges of mismanagement, bureaucracy, wastage, incompetence, and irresponsibility by directors and employees. All the stated problems are an indication of lack of commitment and also leadership issues.
Leadership is complex because it is studied in different ways that entail different definitions. In this case, it can be defined as the process of a leader communicating ideas, gaining acceptance of the vision, and motivating followers to support and implement the ideas through others. A leader always has the ability to influence others and may not necessarily be a manager, whereas another person can possess leadership qualities and also be a manager. Employee commitment is the psychological attachment and the resulting loyalty of an employee to an organization.
Leadership is one of the world’s oldest and most topical issues. The importance of good leadership in producing what is required of an organization is accepted unquestionably, from corporate enterprises to educational institutions. Its key role within the changing education systems of different countries has acknowledged over the past decade or so. Leadership is believed to exist in at every level throughout an organization and usually includes management tasks. Leadership has been given different definitions by different authors. Kotter (1988) views it as the process of influencing people to strive willingly to achieve goals.
Transformational Leadership
It anticipates future trends, inspires to understand and embrace new possibilities, and builds the organization into a community of challenged and rewarded learners. The leaders develop strong emotional bonds with their followers and they possess good visioning and management skills. This leadership style has four components which are described by Bodla and Nawaz, 2010 and Robbins, 2005.
Idealized Influence
Leaders act in such a way that they can be perceived as role models by the people they lead.
Inspirational Motivation (IM)
These leaders arouse the team spirit and show enthusiasm and optimism.
Intellectual Stimulation
The transformational leaders stimulate their followers to be creative and innovative by creating an environment, in which they are forced to think about old problems in new ways.
Individualized Consideration
The leaders act as mentors and coaches. Two-way communications are regular and differences are accepted.
Transactional Leadership
It motivates and directs followers by appealing to their own self-interest. The focus is on basic management processes such as controlling, organizing, and short-term planning. An exchange takes place between leaders and followers to achieve the desired performance.
Contingent Reward (CR)
Leaders explain their expectations, provide the needed resources, set shared goals, and link them to various rewards for doing well.
Management by Exception Active
Here, leaders specify rules and standards. Furthermore, they observe the work of the employees, watch for deviations, and take corrective actions when mistakes or errors occur.
Management by Exception Passive
Leaders do not intervene until problems occur; they wait for things to go wrong before they take action.
LITERATURE REVIEW
This study is to examine leadership styles and employees’ organizational commitment in the Malaysia context. Two types of leadership styles, namely, transformational and transactional leadership styles have been chosen as focus of research to investigate the impact on organizational commitment. This is imperative to ensure the successful management of employees and also to improve productivity and achievements of an organization. The method of this study focuses on manufacturing employees in Malaysia as a population of interest. This study to measure the three dimensions of organizational commitment, namely, affective commitment, continuance commitment, and normative commitment because of the conceptual consistency underlying the definitions that were used in its development and also it was proven to have adequate psychometric properties. A total of 200 questionnaires were distributed. Data were collected through survey questionnaires from subordinates comprising working executives who are currently reporting to lower and middle-level managers. However, only 158 subordinates responded to the survey. The results of the study have indicated that several dimensions of transactional and transformational leadership have a positive relationship with organizational commitment, but the impacts are stronger for transactional leadership style. Implications of the findings, potential limitations of the study, and directions for future research are suggested that the present study has exhibited that transformational leaders have a more significant and stronger relationship with organizational commitment.
Another study determined the relationship between the transformational and transactional leadership styles (as measured by the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire [MLQ] 5X) and organizational commitment (as measured by the Organizational Commitment Questionnaire [OCQ]) in the coal mining industry at a specific site in Phola. The method of this study is a quantitative, cross-sectional survey design with random sampling (n = 88) which was used to collect the necessary data. Both instruments showed acceptable internal consistencies. The study found significant relationships which were found between two variables: Organizational commitment (for the purposes of this article, this refers to affective commitment) and leadership styles (transactional and transformational). The study contributes, managers and human resource practitioners will benefit from the knowledge gained by the study. Line managers should practice transformational leadership to improve commitment, engagement, and satisfaction among their subordinates. The findings of this research add to the body of existing knowledge on transformational leadership and commitment. Valuable insights have been gained on the appropriate leadership style needed to improve commitment in a demanding and under-researched context, namelym the coal mining industry in Phola, Mpumalanga.[1]
A study investigated the relationship between transformational, transactional leadership style, and their dimensions on the organizational commitment among Nigerian banks employees. The targeted population consisted of all employees in banks in Ibadan. The sample was made up of 80 employees from 10 banks randomly selected. The instrument used for the study was tagged MLQ and OCQ. Correlation coefficient and multiple regressions were used to analyze the data. The results of the study showed that there is a positive relationship between transformational, transactional leadership, and organizational commitment. Results also revealed that the impact of transactional leadership styles on the commitment of banking employees in Nigeria are more effective than the transformational style. Therefore, this style of leadership is not significantly inducing employees’ commitment. However, the results of the study showed that the impact of transactional leadership styles on the commitment of banking employees in Nigeria is more effective than the transformational style. The study recommended that since the transactional leadership is based on CR and punishment behavior, therefore, managers should positively reward the employees with praise or recognition when they perform at or above expectations. Similarly, the negative rewarding approach should also be used in the form of correction, coercion, criticism, and/or other forms of punishment, when performance is below the expected standard.[2]
Another study was carried out to examine the effect of leadership and organizational culture on organizational commitment in the context of Malaysian Islamic banking service sector. The method of this study is questionnaire survey which was conducted among 250 employees of an Islamic bank to collect the data which yielded 200 valid responses. The data were analyzed using SPSS software version 19.0. Linear and nultiple regression and SOBEL test were used in testing the research hypotheses. The results reveal that leadership and organizational culture significantly affect organizational commitment. Moreover, leadership plays a significant role in enhancing organizational culture. On the other hand, organizational culture mediates the relationship between leadership and organizational commitment. It implies that leadership style, organizational culture, and organizational commitment all play a key role in the context of Malaysian Islamic Banking industry. This study contributes significantly to practise managers who plan to develop and improve their existing working structures. These results propose a number of vital managerial inferences. To create organizational commitment, an organization needs to have good quality leaders. Any big organizations comprise of great leaders and leadership which is one of the important skills needed to sustain superior.[3]
This study is to examine separately the effects of leadership style and locus of control on organizational commitment. However, researchers have not yet directly measured the relationship between leadership style and organizational commitment as moderated by follower’s locus of control. The study was employed a quantitative methodology, using self-administered surveys comprised of the organization commitment questionnaire, the locus of control questionnaire, and the initiating structure and supervisor consideration sections of Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire, to test the proposed hypotheses. It presented unique opportunities to collect responses from a wide variety of individuals across a wide swath of organizations, demographics, and employee status and tenure. Participant confidentiality was assured by only collecting cursory demographic and employment status information. The findings did not support the proposed hypotheses but did support the previous research that suggests that separately leader style and locus of Control is important drivers of organizational commitment. The results of this study support previous research that suggests that follower attitudes and personality traits have significant impacts on their commitment to the organization. In this study, locus of control was shown to be a significant contributor to followers’ organizational commitment. While the results did not support the hypotheses which proposed the moderating effect of locus of control on the relationship between leader style and organizational commitment, it does suggest that the followers’ disposition deserves adequate attention by leaders.[4]
The same study conducted is to seek the relationship between leadership styles and organizational commitment among Nigerian public university lecturers. Survey research design was employed to collect data from 151 Nigerian public university lecturers currently undergoing their postgraduate studies in selected Malaysian universities. The study established that the leadership styles of top management in Nigerian universities influence organizational commitment among the lecturers. It is hope that the findings of the study will be a guide for the relevant authorities in Nigeria in drafting policies in the universities. This study offers additional insight into how transformational and transactional leadership predict organizational commitment among university lecturers in Nigeria. Furthermore, the pattern of scores obtained from this data suggests that some lecturers perceived their immediate supervisors as not exhibiting the IM behavior levels of transformational leadership behaviors and it was found to be the less important contributor variable. The key element in IM is motivating followers by raising their consciousness on organizational mission and vision. Leaders that are rated high on IM are found to communicate the vision of the organization using gesture and symbols. In addition, IM included engendering trust, inspiring a shared vision, generating enthusiasm, encouraging creativity, and providing coaching this was found to be lacking among the top management in Nigerian universities. Future research will look into the influence of leadership styles on different types of organizational commitment (affective, continuous, and normative) in public universities. In addition, research will also look into sociodemographic factors that explain leadership behaviors among top management in the universities.[5]
This study investigate the impact of the leader’s gender (femininity and masculinity) on transformational leadership and the follower’s organizational commitment (affective, continuance, and normative). The sample consisted of 84 managers of a manufacturing company in eastern India. Participants were randomly assigned to the conditions. The study showed that transformational leadership enhances continuance commitment only when the leader is androgynous and that transformational leadership enhances affective commitment only for the masculine leader. Further, the findings of our study show that transformational leadership enhances continuance commitment only when the leader is androgynous and that transformational leadership enhances affective commitment only for the masculine leader. The managerial and organizational implications of the findings are discussed in this paper. This study aimed to extend this body of work, by examining the impact of gender attributes on transformational leadership and organizational commitment. The results indicate that an androgynous style of leadership has a positive impact on the follower’s continuance commitment and that transformational leadership enhances continuance commitment only when the leader is androgynous.[6]
Another study examined the effects of participative leadership and organizational commitment. The study data were collected from a sample of 70 bank clerks in Alice and King Williams town using participative leadership questionnaire. The result indicated that participative leadership has different effects among two gender groups and it has positive effects on organizational commitment.[7]
The same study explored the relationship between principals’ leadership style, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. A quantitative questionnaire using Likert-type scales was administered to 357 high school teachers and principals in Tehran, Iran. The study samples were selected through stratified sampling technique. The data were tested for reliability and results presented based on the study objectives. The results revealed positive and significant relationships between leadership style, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. This study also clarifies the relationship between job satisfaction and commitment and highlights the crucial role of leadership style in teachers’ job satisfaction and commitment. Hence, the school principals should select the best leadership style according to the organizational culture and employees’ capacity. Implications of the study are discussed in relation to managers and principals, as well as to policymakers at the educational level.[8]
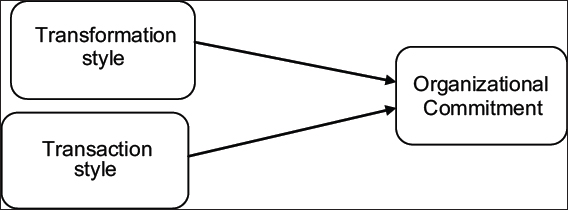
The researchers have generated the following conceptual framework after reviewing several literatures.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Good leadership style has great influence on organizational commitment, which includes principles’ organizational strategy, quality improvement measures, and skills. The conceptual framework for this study is useful various ways, and thus, following hypothesis is generated from the discussion of the literature.
H1: There is a significant relationship between transformational leadership and organizational commitment at UNISO in Mogadishu-Somalia.
H2: There is a significant relationship between transactional leadership and organizational commitment at UNISO in Mogadishu-Somalia.
METHODOLOGY
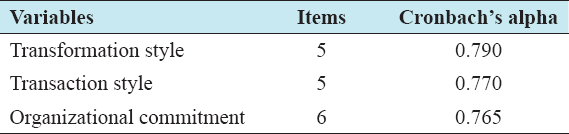
This study was conducted through case study method to examine the role of leadership style on organizational commitment at UNISO in Mogadishu-Somalia. The study utilized regression and correlation analysis to answer the research objectives and to test the research hypothesis. The researchers utilized convenient sampling to collect 95 from full-time lecturers. These respondents were provided a questionnaire with three main construct which measuring transformation style, transaction style, and organizational commitment. The researchers’ utilized Cronbach’s alpha to investigate the internal consistency of the questionnaires collected from the respondents. All variables of the study gained high inside reliability as shown in Table 1, and this allows to make further analysis and discussion.
Table 1: Reliability test
DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
Demographic Profile
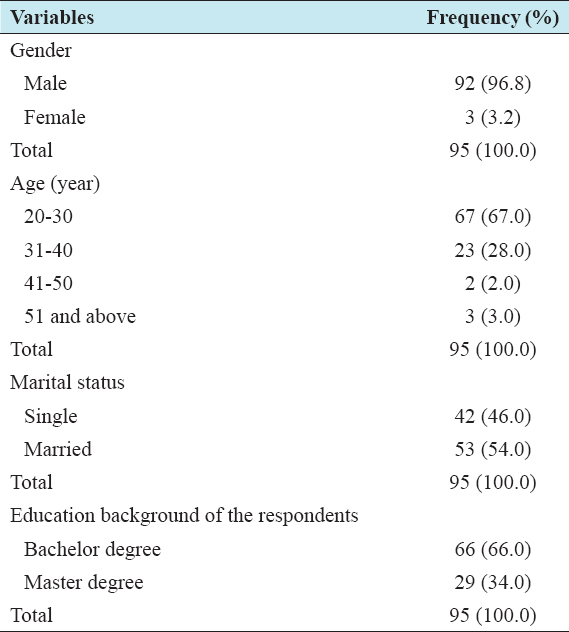
According to the gender respondents, 96.8% were male while 3.2% was female. 67.0% of the respondent’s age was between 20 and 30 years old, 28.0% was between 31 and 40 years, 2.0% was between 41 and 50 years, while 3.0% were above 51 years. In terms of the marital status of the respondents, 54.0% were married while 46.0% were single. In terms of educational background, 4.0% were secondary level, 20.0% of the respondents had diploma certificate, 66.0% of the respondents were bachelor degree, and 34.0% were master degree level [Table 2].
Table 2: Demographic of the respondents
Correlation Analyse between the Two Variables
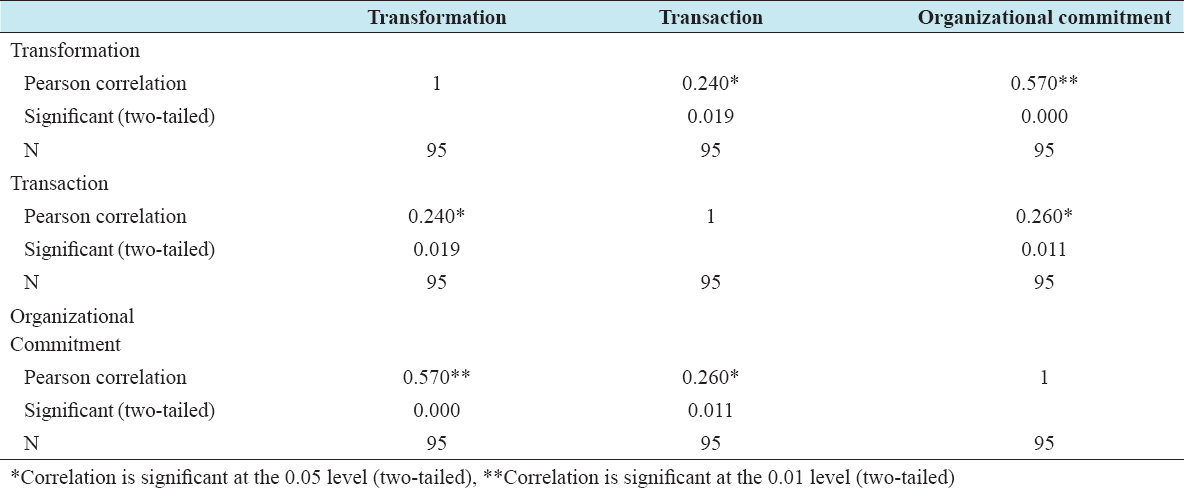
Table 3 summarizes the correlation analyse among the variables. This study has two main objectives. The first objective of this study was to identify the relationship between transformation style and organizational commitment. The result indicated that there is a positive relation between transformation style and organizational commitment (r = 0.570 and P > 0.05). The second objective of this study was to examine the relationship between transaction style and organizational commitment. The result showed positive relationship (r = 0.260 and P > 0.05). In general, this study found that there is a good positive relationship that is between the two dimension of independent variable and dependent variable.
Table 3: Correlations analyse between the variables
Regression Analysis
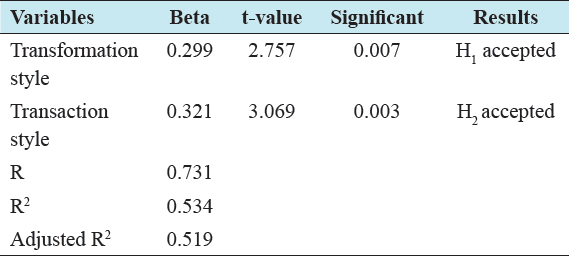
This study investigated the role of leadership style on organizational commitment at UNISO in Mogadishu-Somalia. Two hypotheses were developed after reviewing the literature, to test the research, hypotheses were employed the linear regression analysis. The researchers checked regression hypothesis before taking place to further analysis. The dependent variable which is organizational commitment was normally distributed across all independent variable. Two hypotheses were developed after reviewing the existing literature: H1 confirmed that there is a positive relationship between transformation style and organizational commitment at UNISO. H2 asserted that there is a positive relationship between transaction style and organizational commitment at UNISO in Mogadishu, Somalia [Table 4].
Table 4: Regression analysis
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
This section explains the conclusion of the research of leadership style and organizational commitment. Leadership is measured in terms of transformation and transaction style. This calls for the improvement of leadership style on organizational commitment. Given the consistent interaction between the dimensions of leadership style, the findings suggested that leadership could support organizational commitment using transformation and transaction styles, the first dimension of independent variable which transformation style has a positive relationship with organizational commitment, and the second dimension of which transaction style has positive relationship with organizational commitment. In reference to the result and findings, it is revealed that organizational commitment has a positive relationship with the two dimensions of independent variable.
There are no doubts about the significant role of leadership style on organizational commitment. Thus, the results of this study have some relevance on leadership training, policymakers for educational institutions. The following recommendation can be made based on the findings of the study, to promote commitment. Somali University managers should create open and friendly climate in their institutions, in which lecturers can freely express and share their opinions and collaborations on important decisions. This will reduce stress and increase lecturers’ activity. For university managers, to function in the most effective way, it is recommended that managers must avail themselves to improve organizational commitment.[8]
It is hoped that the results will stimulate further investigation into other equally important aspects affecting leadership style. This study was restricted to one construct of work-related behaviors - leadership style on organizational commitment [Figure 1]. Hence, further research in the area could extend to cover other constructs which also relate to employee commitment.
Figure 1: Structural analysis
Source: Researchers, 2017
Much more research is needed at educational institutions. It could be replicated in different categories of tertiary education. Further studies could also be conducted using private institutions from a wider variety of backgrounds as well as a comparative analysis between all employees. Yet, another area that demands attention is leadership and employee commitment.[9]
Therefore, Somali University managers hoping to enhance organizational commitment should consider the following:
-
Managers should provide effective leadership style for lecturers that will improve productivity and organizational commitment.
-
Managers should provide leadership style-based system of their teachers to better effectiveness.
-
Managers should promote their lecturers to better satisfy as to enhance organizational commitment and quality of teaching.
-
Managers should create information sharing system that allows improving lecturer competence and organizational commitment.