CASE REPORT
Preventing deadly diseases using vaccines is one of the most powerful technologies in protecting human health care.[1] Designing effective vaccines for certain diseases such as tuberculosis and human immunodeficiency virus infections has been failed due to incorrect targeting of antigens into the immune cells.[2-5] The problem of targeting of antigens into the immune system can be attributed by molecular adjuvants. Molecular adjuvants are non-antigen components which carry and deliver the vaccine to the immune system to increase the effectiveness of specific antigens.[6-15] The first vaccine adjuvant “aluminum salts” are approved by food and drug administration, the United States in 1930, and other few molecules have been approved later for human use.[16,17] The interest in the identification of molecular adjuvants has been rapidly increased due to the need for developing better vaccines which can be attributed by adding proper molecular adjuvants.[18] In the recent years, biological text mining from peer-reviewed literature has provided valuable insights into the scientific discoveries and managing health-related issues.[19] In addition, the availability of PubMed database leads one to explore large biomedical literature for effective knowledge management.[20,21]
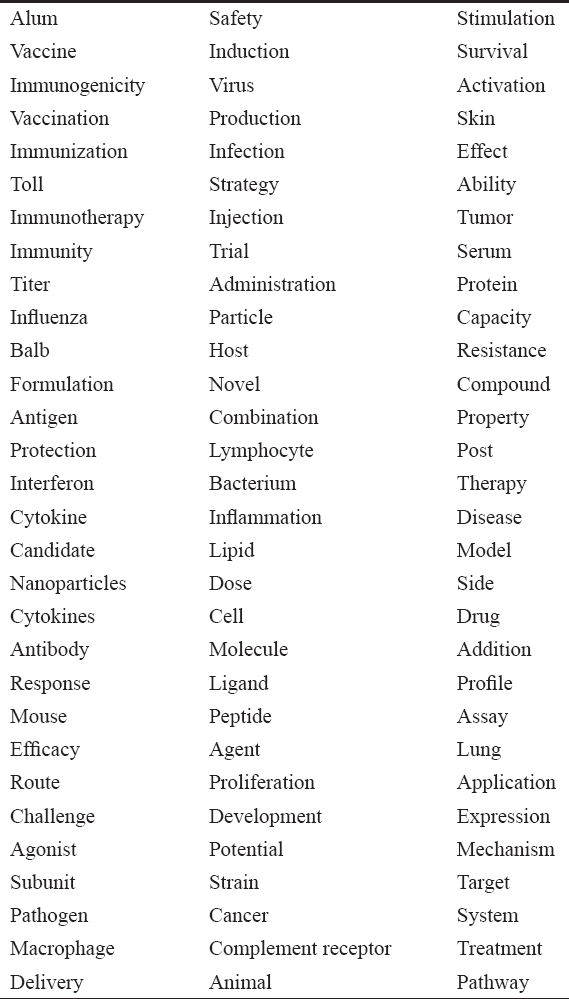
Considering the above facts, we have performed a systematic search on PubMed, a medical bibliographic database with the keyword “Molecular Adjuvants” which resulted in 9692 hits. Further, we have identified frequent nearer terms of the domain (here, the domain is molecular adjuvants) from the 9692 PubMed abstracts, and the results are shown in Table 1. There are ninety frequent nearer terms found in PubMed abstracts which are ranked by the PubMed Ranker tool. The PubMed Ranker tool ranks the frequent nearer terms based on the score.[22] The top five nearer terms such as alum, vaccine, immunogenicity, vaccination, and immunization, respectively, clearly indicate that the molecular adjuvants play a vital role in the immune system. The terms such as influenza, cancer, and tumor, respectively, are observed and represent that the reports are available in the literature about the use of molecular adjuvants in the above diseases.
Table 1: Frequent nearer terms of the domain “Molecular Adjuvants”
Interestingly, the term complement receptor is found as frequent nearer term of molecular adjuvants. In our previous work, we have shown that the molecular adjuvants present in our body interact with complementary receptors to facilitate the development of effective immune response.[23] The binding efficiency of molecular adjuvants (IgGFc, GMCSF, and C3d) with complementary receptors (CR1, CR2, and CR3) was studied in silico and in vivo by our research group. Through the article, we insist that the investigation of the complex formation of molecular adjuvants with complementary receptors and also using of molecular adjuvants along with the vaccines will help to uncover the role of structural organization of these molecules which ultimately pave the way to design better vaccines in the near future.