INTRODUCTION
Project management has gained popularity as a distinct management concept used to drive not only business objectives but also the economic development agenda of developing countries including Ghana. Several programs in Ghana, such as real estate development, event planning, product development, and infrastructure development, especially those tied to foreign aid from development partners and Ghana’s own development policy programs such as the presidential special initiatives (Ghana Investment Promotion Centre, 2001) and the Ghana Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers I and II (National Development Planning Commission, 2002; 2005), all lay heavy emphasis on the use of projects and project management as a tool to optimize the rate of success. The project management as the discipline of planning, organizing, and managing resources to bring about the successful completion of specific project goals and objectives.
A project is a sequence of unique, complex, and connected activities having one goal or purpose that must be completed by a specific time, within budget, and according to specification. This can be contrasted from a routine set of activities or daily operations which are intended to be continuous process without a planned end. Projects are also characterized by general attributes such as the purpose, life cycle, uniqueness, interdependencies, and conflict also defined a project as a unique investment of resources to achieve specific objectives, such as the production of goods or services, to make a profit or to provide a service for a community. A project is an irreversible change with a life cycle and defined start and completion dates. A key characteristic of projects is the role played by a key actor aptly named as project manager. While the project manager is central to the process of project management, s/he is only as good as the project team s/he leads. Thus, it might be an underestimation to propound that the success or otherwise of a project depends solely on the project manager.
To ensure the success of projects, the project manager must have the requisite knowledge of project management, which is defined as the planning, organization, monitoring, and control of all aspects of a project and the motivation of all involved to achieve project objectives safely and within defined time, cost, and performance. It is also the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. In Pinkerton’s (2003) view, project management harnesses the competencies of various individuals, grouping them together and enabling them to achieve the objectives of the project and ensure the success of the project. Quality is a key factor in assessing the success of projects and project management practices.
Quality is considered an important outcome of a project since the performance measures of projects are usually based on time, cost, and quality, also known as the iron triangle. Quality has different attributes - both subjective and objective - some of which are difficult or impossible to quantify. The comprehensive approach to the assessment of project quality to include the traditional project success measures such as cost, schedule, and safety, as well as measures such as customer satisfaction, leadership, employee involvement, teamwork, training, and responsiveness. The dual system of measuring project quality using ratings from what he termed “conventional project quality” and “contemporary project quality.” While “conventional project quality” deals with the extent to which the customer’s requirements are met with respect to the budget, schedule, and technical specifications, “contemporary project quality” is subjective in nature and involves a qualitative assessment of customers and project team members as to how the project is meeting their expectations with regard to issues such as: The communication of goals and values; peer review; customer expectations; partnering; and quality awards. For engineering or construction projects, and analogous procedure which assesses “earned quality” as a means of managing the build-up of quality in a project during the design and construction phases.
Defining project success poses another challenge in understanding project management and consequently assessing its performance. It is generally accepted, however, that the success or otherwise of a project can be defined through the convergence of the ability of the process to meet the technical goals of the project while not deviating from the three constraints of scope, time, and cost; the usefulness of the project as perceived by beneficiaries and sponsors as well as the project team; and the performance of the project. By such a definition, project success or failure can only be effectively measured at the completion of the project.
This is concurred with the study by definition of project success which measures success or failure by the elements of the project log-frame, and thus, the effective utilization of the project output. Projects generally fail as a result of poor planning, constant changes in the scope, and consequently, deadline and budget, as well as the lack of monitoring and control. Five maxims of measuring project satisfaction regardless of project scope, size, or duration which are delivering the product that the customer desires or needs; delivering quality consistent with price; delivering the project within the timeframe stipulated by the customer; delivering the desired degree of feedback that the customer desires; and having a system of conflict resolution that is fair to both the customer and the development team.
The distinguished between project success, which is measured against the overall objectives of the project, and project management success measured against the widespread and traditional measures of performance against cost, time, and quality. Best practices for project management which was believed to contribute to project success. These include: Project mission - the initial clarity of goals and general direction; top management support - the willingness of top management to provide the necessary resources and authority for project success; project schedule/plans - a detailed specification of individual action steps required for project implementation; client consultation communication, consultation, and active listening to all impacted parties; personnel - recruitment, selection, and training of the necessary personnel for the project team; technical tasks - availability of the required technology and expertise to accomplish the specific technical action steps; client acceptance - the act of “selling” the final product to its ultimate intended users; monitoring and feedback - timely provision of comprehensive control information at each phase in the implementation process; communication - the provision of an appropriate network and necessary data to all key actors in the project implementation; and trouble shooting ability to handle unexpected crises and deviations from plan. Over the years, a number of researchers, have concurred that these practices do ensure effective and successful project management.
In general, critical success factors are a set of project variables or factors that are strongly correlated to project success, and whose maximization or minimization, depending on whether they are favorable or unfavorable, will lead to project success. The critical success factors are the limited number of areas in which satisfactory results will ensure successful competitive performance for the individual, department, or organization. They are the few key areas where things must go right for the business to flourish. If results in these areas are not adequate, the organization’s efforts for the period will be less than desired. The concluded that, generally, good planning, clear responsibility and accountability, and schedule control as well as Project leadership and Governance, and Communications are key areas of successful projects. This means that a clear project plan, a plan for risk management, and the commitment and support from stakeholders are the critical success factors for project management.
According to the PMI, 2008, body of knowledge projects, which are temporary endeavours undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives within a defined scope, budget and timeframe, typically go through a life cycle. The project life cycle, which is a logical sequence of activities to accomplish the project’s goals, is made up five stages, namely, the project initiation stage, the project planning stage, the project execution stage, the monitoring and controlling stage, and the project closure stage. Attention to detail, along with the involvement of key stakeholders and proper documentation at each stage, ensures the success and quality of the project. The sequential phases are generally differentiated by the set of activities that are carried out within the phase, the key factors involved, the expected deliverables, and the control measures put in place (PMI, 2004).
Feasibility Study
Feasibility studies are a widely dispersed research tool. Unfortunately, general standards, requirements, or guides on feasibility study design are missing. The aim of any feasibility study is to examine and/or evaluate the possible future success or failure of prospective endeavors (Palvia and Palvia, 1988; Brockman, 2008; Bowen et al., 2009).
Five Areas of Project Feasibility
-
Technical feasibility: Assessment is centered on the technical resources available to the organization. It helps organizations to assess if the technical resources meet capacity and whether the technical team is capable of converting the ideas into working systems. Technical feasibility also involves evaluation of the hardware and the software requirements of the proposed system.
-
Economic feasibility: It helps organizations to assess the viability, cost, and benefits associated with projects before financial resources are allocated. It also serves as an independent project assessment and enhances project credibility, as a result. It helps decision-makers to determine the positive economic benefits to the organization that the proposed system will provide and helps to quantify them. This assessment typically involves a cost/benefits analysis of the project.
-
Legal feasibility: It investigates if the proposed system conflicts with legal requirements like data protection acts or social media laws.
-
Operational feasibility: This involves undertaking a study to analyze and determine whether your business needs can be fulfilled using the proposed solution. It also measures how well the proposed system solves problems and takes advantage of the opportunities identified during scope definition. Operational feasibility studies also analyze how the project plan satisfies the requirements identified in the requirements analysis phase of system development. To ensure success, desired operational outcomes must inform and guide design and development. These include such design-dependent parameters such as reliability, maintainability, supportability, usability, disposability, sustainability, affordability, and others.
-
Scheduling feasibility is the most important for project success. A project will fail if not completed on time. In scheduling feasibility, we estimate how much time the system will take to complete, and with our technical skills, we need to estimate the period to complete the project using various methods of estimation.
Planning Activities
The important of the planning provided by a project manager is to avoid any problems during the process of construction project. In planning activities, the project manager can forecast any incremental of budget if completed projects exceed the expected time. Project managers need to provide planned work schedule so that every part of the work must be completed according to the plan. Besides that the project manager also has the responsibility to manage the budget that has been provided from the client or developer to complete the construction project. Strategic planning is an organizational management activity that is used to set priorities, focus energy and resources, strengthen operations, ensure that employees and other stakeholders are working toward common goals, establish agreement around intended outcomes/results, and assess and adjust the organization’s direction in response to a changing environment. It is a disciplined effort that produces fundamental decisions and actions that shape and guide what an organization is, who it serves, what it does, and why it does it, with a focus on the future. Effective strategic planning articulates not only where an organization is going and the actions needed to make progress but also how it will know if it is successful.[1]
Human Resource Management (HRM)
Since 1980s, HRM strategy has become an important topic for the management area; HRM strategy has achieved its prominence because it provides competitiveness and promotes managerial efficiency in the business area. The rise of HRM in the 1980s brought managerial scholars to the link between the management of people and performance. A number of attempts were made to put empirical facts with the theoretical bones of the knowledge-based firms and the specific HRM views concerning how the systems on HR practice, which can make an increment on the organizational performance. The approach that focuses on individual HR practices and the link with the performance continued since early 1990s.
HRM is used in a global context which contains: (a) Specific human resource practices such as recruitment, selection, and appraisal, (b) formal human resource policies, which direct and partially constrain the development of specific practices, and (c) overarching human resource philosophies, which specify the values that inform an organization’s policies and practices.
More recently, organizations consider the HR department as playing a major role in staffing, training, and helping to manage people so that people and the organization are performing at maximum capability in a highly fulfilling manner. In the global business, HRM is increasingly considered a contemporary development to reshape employment relationships as a tool that may have effectively replaced other management traditions such as personnel management and industrial relations.
LITERATURE REVIEW
This paper aims to focus on the pivotal factor of scope which influences the project’s objectives and consequently affects the critical success factors of a project. A formal documentation of scope is essential to keeping a project on track. The purpose of the research is to explore the proposition that a recognition of the scope in the success of projects. A secondary research is used in this paper. In this regard, past relevant researches have been reviewed generally dealing with project success and scope in particular. The research depicts the relationship between project and product successes. It is concluded that a better appreciation of the distinction between project and product scope can bring a higher possibility of project success.[2]
The purpose of this paper is to describe the conceptual framework of an ongoing PhD research, which seeks to develop a procedure that can help the project management team integrate stakeholders’ perspectives into the project scope definition process at the pre-project planning stage, thereby facilitating better project outcomes. The research was carried out by a mixed method (quantitative and qualitative) approach. It was conducted in three main phases. Phase one was studied the relationships and interactions among the project definition elements. The analysis was conducted using two quantitative techniques: Interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and analytical network process. ISM is capable of formulating and constructing the relationships network between elements. After formulating the relationships network, the significant weight of each element that accounts for the interaction among them was determined by prioritizing and weighting elements. The study suggests that project scope definition practices and stakeholders’ management are two separate domains, which are often investigated separately. However, project scope definition practices can benefit from stakeholders’ management theories.[3]
The main objective of the study is to identify the influence of project manager’s leadership skill toward successful of a construction project. To achieve the research objectives, a systematic method in conducting this research had been organized. This study has used the concept of questionnaires to ensure that the study is conducted is practical and realistic from the point of view of the various agencies involved in the construction industry. A total of 60 questionnaires given to the respondents involved in the construction industry in Perak. Target population is 60 respondents but the sampling size is only 33 respondents. The scale used in the questionnaire is based on Likert Scale. The study concluded that project manager leading characteristics influence the success of the project positively, and it can be acquired through never-ending training and learning.[4]
This paper discusses the issues involved in project success and failure and presents the feedback of 50 undergraduate students who undertook a team project of the project management course. A questionnaire was designed to investigate the factors that contributed to project success and also factors that resulted in project failure. The study found top three factors that cause project success is as follows: User involvement, good planning and estimations, good leadership, and team members’ technical skills. Comparing the case study results with the Standish Group report, and it is obvious that these factors are fundamental and exhibit strong impact on many projects failure. Applying good project management practices would help to avoid these failure factors and lead to project success.[5]
The aim of this article is to highlight the significance of leadership skills that are vital for project managers’ while managing projects effectively and efficiently. An interesting observation has been noted from literature in the field of project management that research on leadership of project managers is still limited even though calls have been made to conduct more research for more than one decade. The literature reveals that project managers must possess essential qualities and competencies of leadership in addition to management skills for effective accomplishments of business and projects results. The project manager must apply right skills at right time and embrace right knowledge for right jobs. A sufficient research is required to develop and authenticate a single model for project manager’s leadership which suits all the projects across the countries as well as all the industries. The impact of project management qualification on project success and career outcome also needs to be addressed in future research.[6]
The study sought to identify and assess the quality of project management practices as well as the critical success factors for projects in Ghana. The study adopted an exploratory approach and utilized a survey method to collect data on project management practices of Ghanaian organizations. Purposive sampling was used in selecting the sample which comprised 200 managers from different economic sectors. Results from the study indicated that the critical factors that contribute to the success of a project include top management support, effective communication, clarity of project purpose and goals, and stakeholder involvement Documentation and dissemination of critical success factors and best practices in project management will improve the quality of project management in Ghana.[1]
This research seeks to find the contribution of these information systems toward project success. The quality of the software, the quality of information output, and the influence of the PMIS user on the project success were tested. Purposive sampling was used and data measured on a Likert scale. The research found that the use of the software to generate quality information needed by the user (project manager) to perform project tasks helped the project managers perform their tasks in a more professional manner, thus increasing the success rate of the project. The three independent variables (quality of software, quality of information output, and influence of the user) were transformed to get a single variable PMIS which had a strong and positive correlation (0.954) with the dependent variable (project success). It was therefore concluded that the use of PMIS helped in the achievement of the project success while respecting the projects constraints and meeting the project objectives.[7]
The purpose of this study is to investigate the critical factors that influence a successful project among manufacturing companies in Penang, Malaysia. In addition, this study is also aimed to explore if project change control plays a role in moderating the relationship between the independent variables and dependent variable identified in this research. This study was carried out using structured questionnaire. “Questionnaire is a popular method of collecting data because researchers can gather information fairly easily and the questionnaire responses are easily coded.” The questionnaire used is adopted from Pinto’s Project Implementation Profile, which has been verified to be reliable and valid. The findings showed that top management support is positively related to indirect project success in manufacturing which is in line with the findings of that a project is likely to be successful if visible support and commitment are present from the top and executive management.[8]
This study aims to measure the recent scenario of the project management success field as a way to better understand this field of research. A bibliometric study was developed with a portfolio of 64 papers about “project management success” collected at the Web of Science (ISI) database, covering the evolution of this topic over the past 5 years (from 2000 to 2014). Articles were analyzed by journal, most cited keywords, citations, cocitations, journals’ impact factors, and abstract analysis. Conclusions pointed out significant authors and journals and also a significant cluster of papers written by Aaron Shenhar, as a relevant source of information to the project management success field. This information may be used by other authors to spur other studies about the project management success subject, not covered by this research.[9]
The paper examined the application of the project management practice in public sector in Nigeria. The PM lifecycles, tools, and techniques were presented. The study was carried out in Lagos because of its metropolitan nature and rapidly growing economy. 23 copies of questionnaire were administered to 23 public institutions in Lagos to generate primary data. The descriptive analysis techniques using percentages and table presentations coupled with coefficient of correlation were used for data analysis. The study revealed that application of PM tools and techniques is an essential management approach that tends to achieve specified objectives within specific time and budget limits through the optimum use of resources. Furthermore, the study noted that there is lack of in-depth knowledge of PM tools and techniques in public sector institutions sampled, and also, high cost of application was also observed by the respondents. The study recommended among others that PM tools and techniques should be applied gradually, especially in old government institutions, where resistance to change is perceived to be high.[10]
The main objective of this research is to identify the importance of project manager and project team role for the successful implementation of EMP in the Malaysian construction industry. Using the survey method, questionnaires were sent to the Malaysian construction stakeholders that included consultants, contractors, and clients, and 122 questionnaires were analyzed. This study found that most of the construction stakeholders agreed that project team commitment, project manager’s leadership skills, and communication system effectiveness are very important to ensure the success of EMP. The results further demonstrate that three of the independent variables - project manager and project team competency, project management aspects, and procurement related factors have significant relationships with EMP Success.[11]
After reviewing several literatures, the researcher generated the following hypothesis.
Conceptual Framework
-
H1: There is positive relationship between feasibility study and project success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia.
-
H2: There is positive relationship between planning activities, tasks, schedules, budgets, and project success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia.
-
H3: There is positive relationship between managing human resource and project success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia.
METHODOLOGY
This study was conducted through survey study method to examine the role of project management in achieving success in Mogadishu-Somalia. The study utilized regression and correlation analysis to answer the research objectives and to test the research hypothesis.
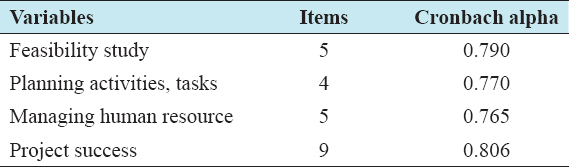
The researchers utilized convenient sampling to collect 100 employees from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia. These respondents were provided a questionnaire with four main construct which measuring feasibility study, planning activities, managing human resource, and project success. All variables of the study gained high inside reliability as shown in Table 1, and this allows as to make further analysis and discussion.
Table 1: Reliability test
DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
Demographic Profile
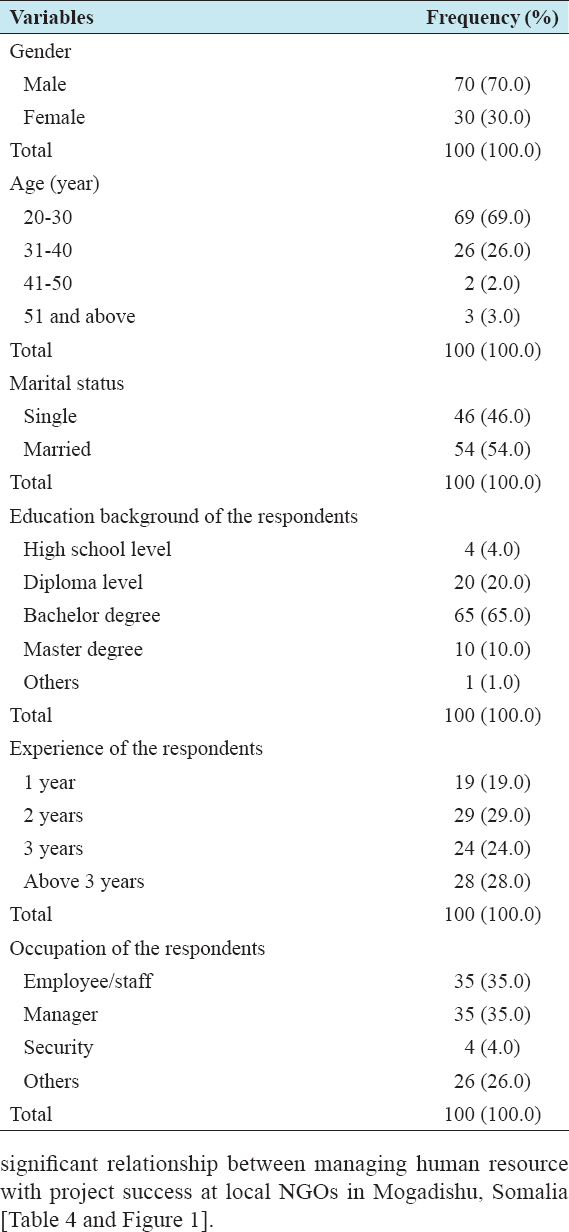
According to the gender respondents, 70.0% were male while 30.0% was female. 69.0% of the respondent’s age were between 20 and 30 years old, 26.0% were between 31 and 40 years, 2.0% were between 41 and 50 years, while 3.0% were above 51 years. In terms of marital status of the respondents, 54.0% were married while 46.0% were single. In terms of educational background, 4.0% were secondary level, 20.0% of the respondents had diploma certificate, 65.0% of the respondents were bachelor degree, and 10.0% were master degree level, while 1.0% had other certificate. In terms of experience, 19.0% of the respondents had 1 year experience, 29.0% of the respondents had 2 years experience, and 24.0% of the respondents had 3 years experience, while 28.0% of the respondents had more than 3 years experience. In terms of occupation of the respondents, 35.0% of the respondents were employee/staff, 35.0% of the respondents were managers, and 4.0% of the respondents were security, while 26.0% were other people [Table 2].
Table 2: Demographic of the respondents
Correlation between the Variables
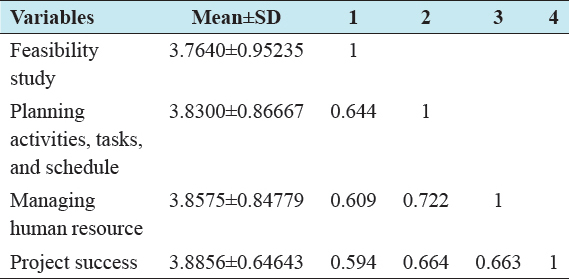
Table 3 shows the result of correlation analyzes of the relationships among feasibility study, planning activities, managing human resource, and project success at local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia. Feasibility study has positive relationship with project success (r = 0.594 and P < 0.01). The second objective of this study was to identify the relationship between planning activities and project success at r = 0.664 and P < 0.01. The third objective was to examine the relationship between managing human resource and project success at r = 0.663 and P < 0.01.
Table 3: Correlation analyzes
Regression Analysis
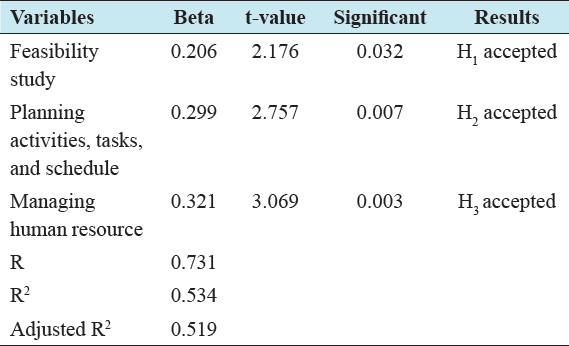
This study investigated the role of project management in achieving success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia. Three hypotheses were developed after reviewing the literature, to test the research, hypotheses were employed the linear regression analysis. The researchers checked regression hypothesis before taking place to further analysis. The dependent variable which is project success was normally distributed across all independent variable. Three hypotheses were developed after reviewing the existing literature: H1 confirmed that there is positive relationship between feasibility studies with project success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia, H2 asserted that there is positive relationship between planning activities with project success, while H3: There is a significant relationship between managing human resource with project success at local NGOs in Mogadishu, Somalia [Table 4 and Figure 1].
Table 4: Regression analysis
Figure 1: The role of project management
DISCUSSION
The current study investigated the role of project management in achieving success from local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia; the paper had three main objectives which are: (1) To determine the influence of feasibility study and project success, (2) to identify the impact planning activities and project success, and (3) to examine the role of managing human resource and project success at local NGOs in Mogadishu-Somalia. The researchers employed convenient sampling to collect 100 respondents from local NGOs in Mogadishu. The result of correlation coefficient revealed that project success (dependent variable) had significant positive influence with three independent variables, namely, feasibility study, planning activities, and managing human resource. The result of regression analysis found that three constructs had statistically significant, positive, and direct effect on project success. The standpoint of this study emphasizes the important role of innovation performance and environmental performance when addressing the link between project management and achieving success. Subsequently, incorporation of the green element in project management will certainly enhance sustainable improvements which benefit long-term organizational performance.